@WFS,World Fossil Society,Riffin T Sajeev,Russel T Sajeev
Birds of a Feather: Neanderthal Exploitation of Raptors and Corvids
Citation: Finlayson C, Brown K, Blasco R, Rosell J, Negro JJ, Bortolotti GR, et al. (2012) Birds of a Feather: Neanderthal Exploitation of Raptors and Corvids. PLoS ONE 7(9): e45927. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0045927
Editor: Michael D. Petraglia, University of Oxford, United Kingdom
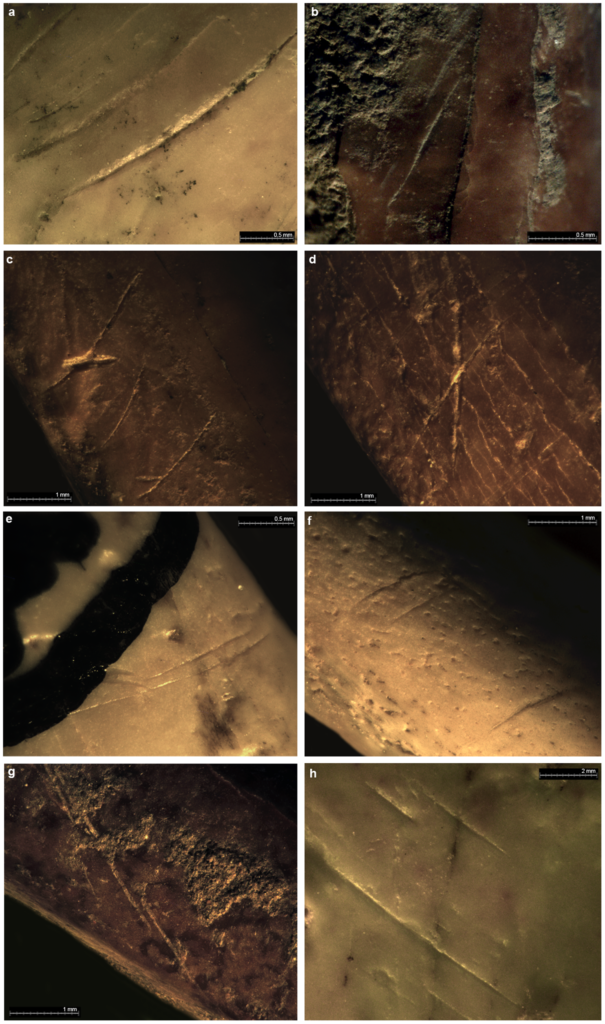
Examples of cut-marks from Gibraltar sites.
a) distal diaphysis of Pyrrhocorax pyrrhocorax humerus (Gor’96 No. 87); b) proximal diaphysis of Pyrrhocorax pyrrhocorax humerus; c) proximal diaphysis of Pyrrhocorax pyrrhocorax humerus (GOR’96 NO. 299); d) distal diaphysis of Milvus milvus radius (GOR’00/B8/NIV/205); e) middle shaft of Pyrrhocorax pyrrhocorax tarsometatarsus (Ibex 94 No. 24); f) middle shaft of Pyrrhocorax pyrrhocorax femur (Ibex 94 No. 166); g) proximal diaphysis of Pyrrhocorax graculus ulna (GOR’00/B5/NIV/57); h) distal diaphysis of Gyps fulvus ulna (Van 96 No. 209A).
The hypothesis that Neanderthals exploited birds for the use of their feathers or claws as personal ornaments in symbolic behaviour is revolutionary as it assigns unprecedented cognitive abilities to these hominins. This inference, however, is based on modest faunal samples and thus may not represent a regular or systematic behaviour. Here we address this issue by looking for evidence of such behaviour across a large temporal and geographical framework. Our analyses try to answer four main questions: 1) does a Neanderthal to raptor-corvid connection exist at a large scale, thus avoiding associations that might be regarded as local in space or time?; 2) did Middle (associated with Neanderthals) and Upper Palaeolithic (associated with modern humans) sites contain a greater range of these species than Late Pleistocene paleontological sites?; 3) is there a taphonomic association between Neanderthals and corvids-raptors at Middle Palaeolithic sites on Gibraltar, specifically Gorham’s, Vanguard and Ibex Caves? and; 4) was the extraction of wing feathers a local phenomenon exclusive to the Neanderthals at these sites or was it a geographically wider phenomenon?. We compiled a database of 1699 Pleistocene Palearctic sites based on fossil bird sites. We also compiled a taphonomical database from the Middle Palaeolithic assemblages of Gibraltar. We establish a clear, previously unknown and widespread, association between Neanderthals, raptors and corvids. We show that the association involved the direct intervention of Neanderthals on the bones of these birds, which we interpret as evidence of extraction of large flight feathers. The large number of bones, the variety of species processed and the different temporal periods when the behaviour is observed, indicate that this was a systematic, geographically and temporally broad, activity that the Neanderthals undertook. Our results, providing clear evidence that Neanderthal cognitive capacities were comparable to those of Modern Humans, constitute a major advance in the study of human evolution.
@WFS,World Fossil Society,Riffin T Sajeev,Russel T Sajeev



 June 29th, 2018
June 29th, 2018  Riffin
Riffin  Posted in
Posted in 