Computer simulations conducted at the U.S. Department of Energy’s Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab) could help scientists make sense of a recently observed and puzzling wrinkle in one of nature’s most important chemical processes. It turns out that calcium carbonate — the ubiquitous compound that is a major component of seashells, limestone, concrete, antacids and myriad other naturally and industrially produced substances — may momentarily exist in liquid form as it crystallizes from solution.
Calcium carbonate is a huge player in the planet’s carbon cycle, so any new insight into how it behaves is potentially big news. The prediction of a dense liquid phase during the conversion of calcium carbonate to a solid could help scientists understand the response of marine organisms to changes in seawater chemistry due to rising atmospheric CO2 levels. It could also help them predict the extent to which geological formations can act as carbon storage reservoirs, among other examples.
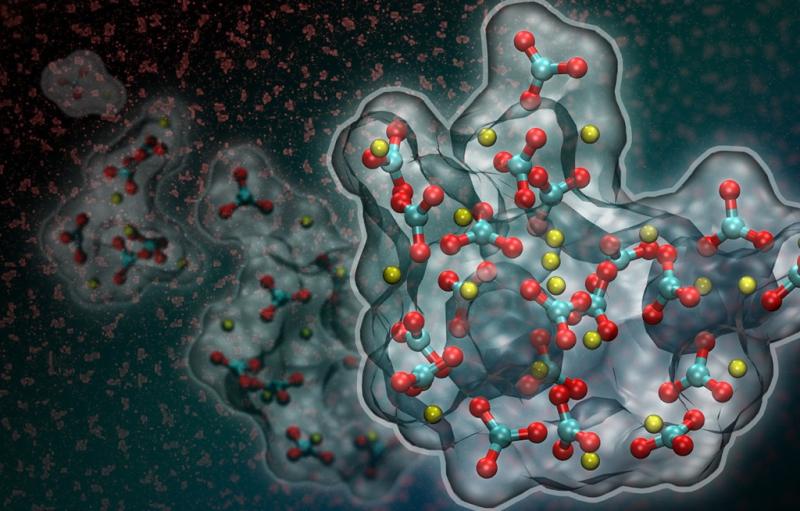
Artistic rendition of liquid-liquid separation in a supersaturated calcium carbonate solution. New research suggests that a dense liquid phase (shown in red in the background and in full atomistic detail based on computer simulations in the foreground) forms at the onset of calcium carbonate crystallization. (Credit: Berkeley Lab)
The research is published in the August 23 issue of the journal Science. It was performed in support of the Center for Nanoscale Control of Geologic CO2, an Energy Frontier Research Center established at Berkeley Lab by the U.S. Department of Energy.
The research may also reconcile some confounding experimental observations. For more than a century, scientists believed that crystals nucleate from solution by overcoming an energy barrier. But recent studies of calcium carbonate revealed the presence of nanoscopic clusters which, under certain conditions, appear to circumvent the barrier by following an alternative aggregation-based crystallization pathway.
“Because nucleation is ubiquitous in both natural and synthetic systems, those findings have forced diverse scientific communities to reevaluate their longstanding view of this process,” says the study’s co-corresponding author Jim De Yoreo, formerly of Berkeley Lab and now a scientist at Pacific Northwest National Laboratory.
The Berkeley Lab-led team used molecular dynamics simulations to study the onset of calcium carbonate formation. The simulations predict that in sufficiently supersaturated calcium carbonate solutions, nanoscale dense liquid droplets can spontaneously form. These droplets then coalesce to form an amorphous solid prior to crystallization.
The findings support the aggregation-based mechanism of calcium carbonate formation. They also indicate that the presence of the nanoscale phase is consistent with a process called liquid-liquid separation, which is well known in alloys and polymers, but unexpected for salt solutions.
“Our simulations suggest the existence of a dense liquid form of calcium carbonate,” says co-corresponding author Adam Wallace. He conducted the research while a post-doctoral researcher in Berkeley Lab’s Earth Sciences Division, and is now an assistant professor in the Department of Geological Sciences at the University of Delaware.
“This is important because it is an as-yet unappreciated component of the carbon cycle,” adds Wallace. “It also provides a means of explaining the unusual presence of nanoscale clusters in solution within the context of established physical mechanisms.”
This research was supported by the U.S. Department of Energy’s Office of Science through the Energy Frontier Research Center program established in 2009. The work was conducted at Berkeley Lab’s Molecular Foundry, a Department of Energy national user facility. The research also used resources of the Department of Energy’s National Energy Research Scientific Computing Center, which is located at Berkeley Lab.



 August 24th, 2013
August 24th, 2013  Riffin
Riffin  Posted in
Posted in  Tags:
Tags: 