Background
The holotype of the theropod non-avian dinosaur Microraptor gui from the Early Cretaceous of China shows extensive preservation of feathers in a halo around the body and with flight feathers associated with both the fore and hindlimbs. It has been questioned as to whether or not the feathers did extend into the halo to reach the body, or had disassociated and moved before preservation. This taxon has important implications for the origin of flight in birds and the possibility of a four-winged gliding phase.
Methodology/Principal Findings
Examination of the specimen under ultraviolet light reveals that these feathers actually reach the body of the animal and were not disassociated from the bones. Instead they may have been chemically altered by the body tissues of the animal meaning that they did not carbonise close into the animal or more likely were covered by other decaying tissue, though evidence of their presence remains.
Conclusions/Significance
These UV images show that the feathers preserved on the slab are genuinely associated with the skeleton and that their arrangement and orientation is likely correct. The methods used here to reveal hidden features of the specimen may be applicable to other specimens from the fossil beds of Liaoning that produced Microraptor.

Figure 1. The holotype of Microraptor gui, IVPP V 13352 under normal light.
This shows the preserved feathers (white arrow) and the ‘halo’ around the specimen where they appear to be absent (black arrows). Scale bar at 5 cm.
doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0009223.g001
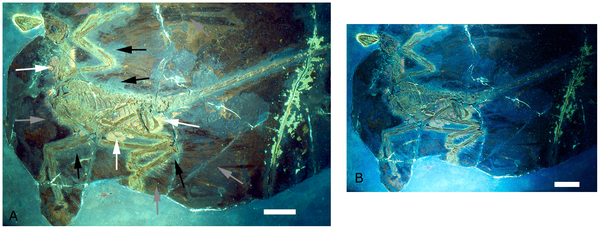
Figure 2. The holotype of Microraptor gui, IVPP V 13352 under UV light.
Different filters were employed for parts A and B, hence the difference in colour and appearance. A also is labeled to indicate the preserved feathers (grey arrows) and the ‘halo’ around the specimen where they appear to be absent (black arrows) as well as phosphatised tissues (white arrows). Scale bars are 5 cm in both A and B.
doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0009223.g002
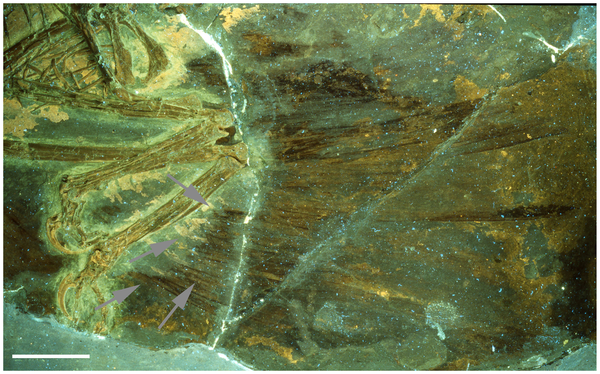
Figure 3. Close up of lower hindlimb of the holotype under UV light.
This shows that the feathers do indeed penetrate the halo (grey arrows) when seen in UV and approach or reach the bones. These are not seen in natural light due to the overlying soft tissues seen in figure 2. Scale bar at 5 cm.
doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0009223.g003
Citation: Hone DWE, Tischlinger H, Xu X, Zhang F (2010) The Extent of the Preserved Feathers on the Four-Winged Dinosaur Microraptor gui under Ultraviolet Light. PLoS ONE 5(2): e9223. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0009223
Editor: Andrew Allen Farke, Raymond M. Alf Museum of Paleontology, United States of America



 October 22nd, 2013
October 22nd, 2013  Riffin
Riffin  Posted in
Posted in  Tags:
Tags: 