This is the best-preserved fossil find yet from the early era of our genus. The particularly interesting aspect is that it displays a combination of features that were unknown to us before the find. The skull, found in Dmanisi by anthropologists from the University of Zurich as part of a collaboration with colleagues in Georgia funded by the Swiss National Science Foundation, has the largest face, the most massively built jaw and teeth and the smallest brain within the Dmanisi group.
Diversity within a species instead of species diversity
Because the skull is completely intact, it can provide answers to various questions which up until now had offered broad scope for speculation. These relate to none less than the evolutionary beginning of the genus Homo in Africa around two million years ago at the beginning of the Ice Age, also referred to as the Pleistocene. Were there several specialized «Homo» species in Africa at the time, at least one of which was able to spread outside of Africa too? Or was there just one single species that was able to cope with a variety of ecosystems? Although the early Homo finds in Africa demonstrate large variation, it has not been possible to decide on answers to these questions in the past. One reason for this relates to the fossils available, as Christoph Zollikofer, anthropologist at the University of Zurich, explains: “Most of these fossils represent single fragmentary finds from multiple points in space and geological time of at least 500,000 years. This ultimately makes it difficult to recognize variation among species in the African fossils as opposed to variation within species.”
As many species as there are researchers
Marcia Ponce de León, who is also an anthropologist at the University of Zurich, points out another reason: paleoanthropologists often tacitly assumed that the fossil they had just found was representative for the species, i.e. that it aptly demonstrated the characteristics of the species. Statistically this is not very likely, she says, but nevertheless there were researchers who proposed up to five contemporary species of early Homo in Africa, including Homo habilis, Homo rudolfensis, Homo ergaster and Homo erectus. Ponce de León sums up the problem as follows: “At present there are as many subdivisions between species as there are researchers examining this problem.”
Tracking development of «Homo erectus» over one million years thanks to a change in perspective
Dmanisi now offers the key to the solution. According to Zollikofer, the reason why Skull 5 is so important is that it unites features that have been used previously as an argument for defining different African “species”. In other words: “Had the braincase and the face of the Dmanisi sample been found as separate fossils, they very probably would have been attributed to two different species.” Ponce de León adds: “It is also decisive that we have five well-preserved individuals in Dmanisi whom we know to have lived in the same place and at the same time.” These unique circumstances of the find make it possible to compare variation in Dmanisi with variation in modern human and chimpanzee populations. Zollikofer summarizes the result of the statistical analyses as follows: “Firstly, the Dmanisi individuals all belong to a population of a single early Homo species. Secondly, the five Dmanisi individuals are conspicuously different from each other, but not more different than any five modern human individuals, or five chimpanzee individuals from a given population.”
Diversity within a species is thus the rule rather than the exception. The present findings are supported by an additional study recently published in the journal PNAS. In that study, Ponce de León, Zollikofer and further colleagues show that differences in jaw morphology between the Dmanisi individuals are mostly due to differences in dental wear.
This shows the need for a change in perspective: the African fossils from around 1.8 million years ago likely represent representatives from one and the same species, best described as Homo erectus. This would suggest that «Homo erectus» evolved about 2 million years ago in Africa, and soon expanded through Eurasia – via places such as Dmanisi – as far as China and Java, where it is first documented from about 1.2 million years ago. Comparing diversity patterns in Africa, Eurasia and East Asia provides clues on the population biology of this first global human species.
This makes Homo erectus the first “global player” in human evolution. Its redefinition now provides an opportunity to track this fossil human species over a time span of 1 million years.



 October 18th, 2013
October 18th, 2013  Riffin
Riffin 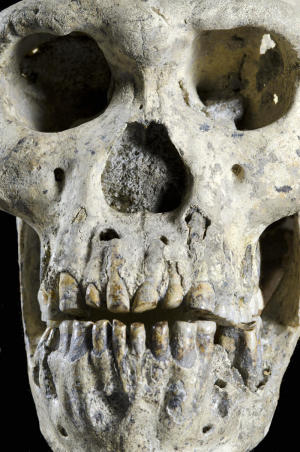
 Posted in
Posted in  Tags:
Tags: 