Imagine how much dental care you’d need if you had 300 or more teeth packed together on each side of your mouth.

Tethyshadros insularis, a hadrosaur. Duck-billed dinosaurs (hadrosaurs), who lived in the Cretaceous period between 90 million and 65 million years ago, sported this unique dental system, which had never been fully understood until it was examined at the microscopic level
Credit: © bepsphoto / Fotolia
Duck-billed dinosaurs (hadrosaurs), who lived in the Cretaceous period between 90 million and 65 million years ago, sported this unique dental system, which had never been fully understood until it was examined at the microscopic level through recent research conducted by Aaron LeBlanc, a University of Toronto Mississauga PhD candidate; his supervisor, Professor Robert Reisz, the University of Toronto Mississauga vice-dean, graduate, and colleagues at the Royal Ontario Museum and the Museum of the Rockies.
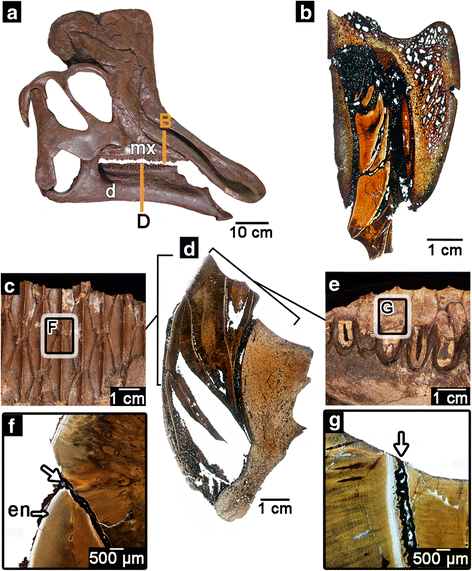
The hadrosaurid dental battery. a skull of the hadrosaurid Corythosaurus (ROM 00868). Image flipped for the figure. b histological thin section through the maxillary dental battery of a hadrosaurid (ROM 00696). c lingual view of the dental battery in the lower jaw. d histological thin section through the dentary dental battery of the hadrosaurid Prosaurolophus (ROM 3500). e occlusal surface of the dentary dental battery. f closeup image of the intersection between two dentary teeth in a battery, showing the infilling of sediment (white arrow) that holds them together. g closeup image of the intersection of two teeth along the occlusal surface of a dental battery showing the infilling of sediment that holds the two teeth together. For (b) and (d), lingual is to the left. d, dentary; en, enamel; mx, maxilla
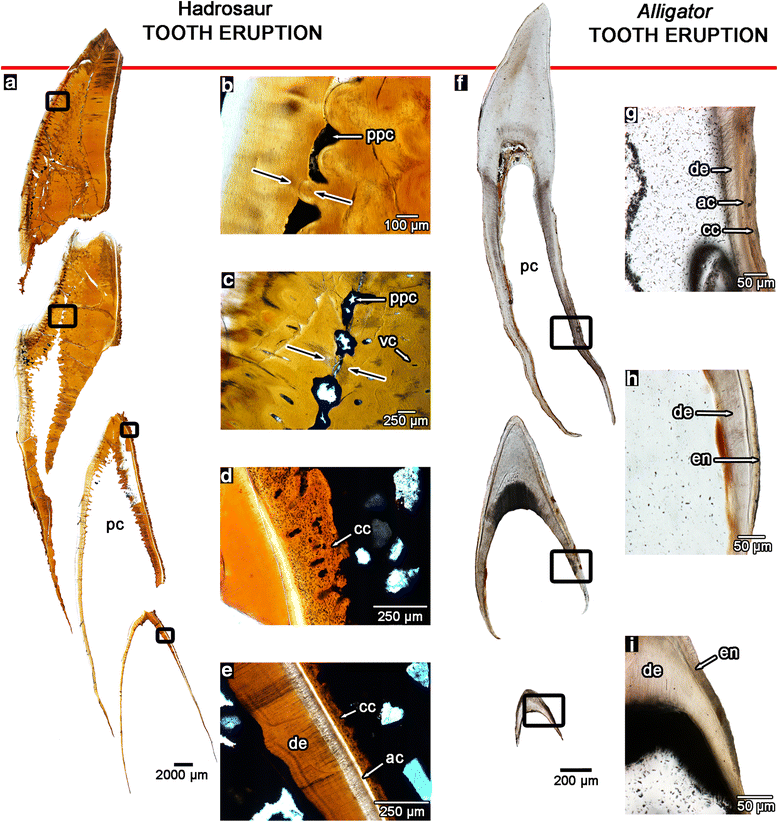
Rather than shedding teeth and replacing them with new ones like other reptiles, hadrosaurs’ mouths contain several parallel stacks of six or more teeth apiece, forming a “highly dynamic network” of teeth that was used to grind and shear tough plant material. Although hadrosaur teeth appear to be fused in place, LeBlanc and his colleagues show that the newest teeth were constantly pushed towards the chewing surface by a complex set of ligaments. When viewed under the microscope, the columns of teeth are not physically touching and are held together by the sand and mud that can get in between the teeth following the decay of the soft ligaments after the animals died.
The hadrosaurid dental battery. a skull of the hadrosaurid Corythosaurus (ROM 00868). Image flipped for the figure. b histological thin section through the maxillary dental battery of a hadrosaurid (ROM 00696). c lingual view of the dental battery in the lower jaw. d histological thin section through the dentary dental battery of the hadrosaurid Prosaurolophus (ROM 3500). e occlusal surface of the dentary dental battery. f closeup image of the intersection between two dentary teeth in a battery, showing the infilling of sediment (white arrow) that holds them together. g closeup image of the intersection of two teeth along the occlusal surface of a dental battery showing the infilling of sediment that holds the two teeth together. For (b) and (d), lingual is to the left. d, dentary; en, enamel; mx, maxilla
“Hadrosaur teeth are actually similar to what we have because our teeth are not solidly attached to our jaws. Like us, hadrosaur teeth would have had some fine-scale mobility as they chewed thanks to this ligament system that suspended the teeth in place,” says Reisz.
As they reached the grinding surface, hadrosaur teeth were essentially dead, filled with hard tissue — unlike humans, whose teeth have an inner core filled with blood vessels and nerves.
“Since the teeth were already dead, they could be ground down to little nubbins,” Reisz says.
The internal anatomy of the hadrosaurid dental battery. a artist’s reconstruction of a portion of the maxillary dental battery, with cutaways in the transverse and coronal planes. For completely labeled reconstruction, see Additional file 3: Figure S2 (illustration by D. Dufault). b magnified image of the junction between primary alveolar bone and the remodelled bone of the jaw. c magnified image of the resorptive front created by the younger teeth within a vertical stack of teeth (direction of resorption indicated by black arrows). d magnified image of the attachment site between the teeth and wall of the socket (direction of periodontal ligament fibers indicated by black arrows). The birefringence in the cellular cementum is caused by the parallel orientations of the Sharpey’s fibers. e magnified image of the occlusal end of the dental battery in thin section showing teeth at various stages of wear. f image of a tooth within the battery in transverse section. ab, alveolar bone; ac, acellular cementum; cc, cellular cementum; de, dentine; en, enamel; Li, lingual; Me, mesial; pc, pulp cavity; ppc, plugged pulp cavity; rl, reversal line
LeBlanc says this tooth structure — with its tough grinding surface — was “well-adapted to break down tough plant material for digestion,” through both shearing and grinding. This adaptation may have contributed to the hadrosaurs’ longevity and proliferation.
Reisz says that hadrosaurs had “probably the most complex dental system ever made.”
“It’s very elegant — not a single brick of teeth working as a solid unit,” he says. “It’s more like chain mail, providing flexibility as well as strength.”
LeBlanc notes that the duck-billed dinosaur has been known for over 150 years and its dental system has long been recognized as unique, but no one had taken a look inside it at the microscopic level previously. He created thin sections of entire dental assemblies from the upper and lower jaws, that he then ground down, polished and examined under a powerful microscope. Working with their museum colleagues, he and Reisz were also able to explore how hadrosaur teeth form in embryos and hatchlings, providing a more complete picture of this unique model of dental evolution and development.
“The amazing thing is how consistently these dental assemblies conform to our hypothesis of how the system works,” LeBlanc says. “Even in the youngest specimens, the same processes that maintained dental assemblies in the adults were visible.”
Citation: University of Toronto. “300 Teeth: Duck-billed dinosaurs would have been dentist’s dream.” ScienceDaily. ScienceDaily, 25 August 2016. <www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2016/08/160825120216.htm>
@WFS,World Fossil Society,Riffin T Sajeev,Russel T sajeev



 September 11th, 2016
September 11th, 2016  Riffin
Riffin 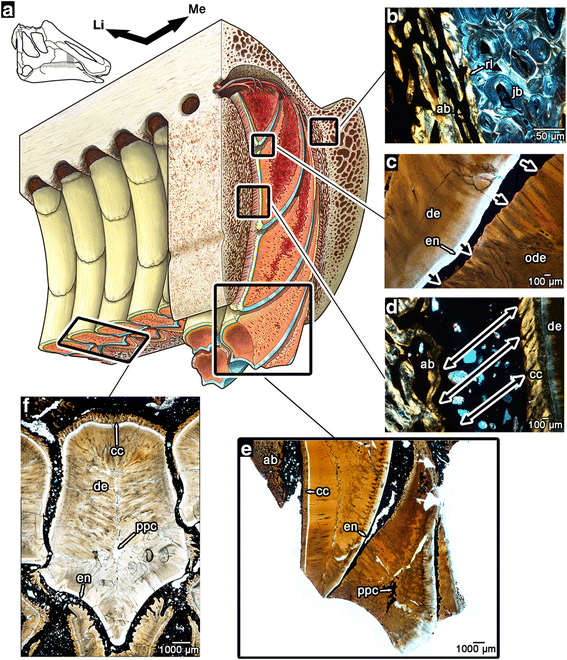
 Posted in
Posted in  Tags:
Tags: 